Conceptually, RAG is simple: You’ve got your LLM but it lacks private information, corporate data or has a data cut-off which is too far in the past. Therefore, you make more data available, usually usig a vector store.
The data that gets loaded into the vector store is usually a curated source of truth. However, not always has the content written in the same way like a user would query for it. As a consequence, RAG might provide imprecise responses and leaving users unsatisfied.
This is where query translation comes in. It basically tries to bridge the gap how information is phrased in the vector store and the way users prompt for that knowledge. The solution is quite simple: Query translation re-formulates the user question in different ways with the goal that hopefully one of the alternative formulations are closer to the content in the vector store.
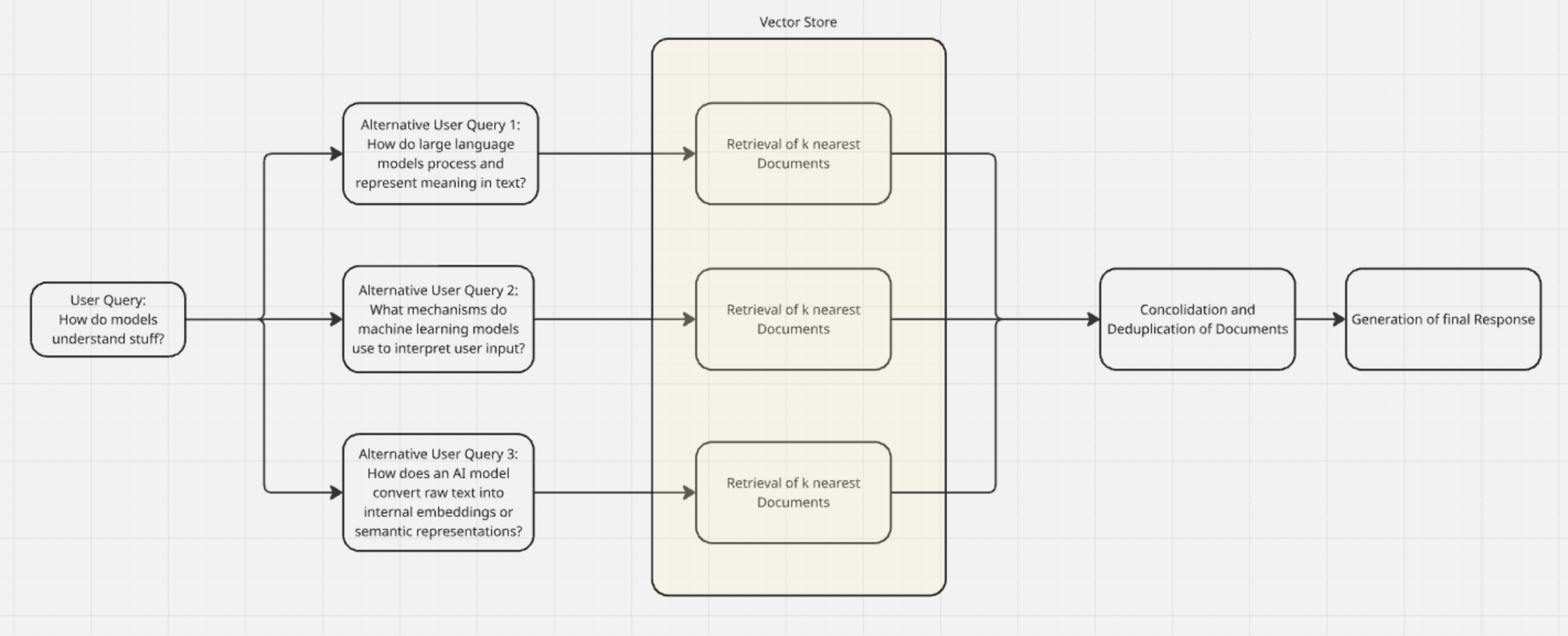
Code example using FAISS and Langchain:
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI, OpenAIEmbeddings
from langchain.prompts import PromptTemplate
from langchain.chains import LLMChain
from langchain_community.vectorstores import FAISS
from langchain.schema import Document
llm = ChatOpenAI(model="gpt-4o-mini")
embed = OpenAIEmbeddings(model="text-embedding-3-small")
texts = [
"Query translation improves retrieval quality by reformulating the search query.",
"RAG systems can benefit from multiple query variations for better recall.",
"Using synonyms in queries increases the probability of matching relevant documents.",
]
vs = FAISS.from_texts(texts, embed)
retriever = vs.as_retriever(search_kwargs={"k": 4})
prompt = PromptTemplate(
input_variables=["question"],
template="""
Generate three semantically diverse reformulations of the following question.\n
Question: {question}\n
Return them as a bullet list.
""",
)
query_gen_chain = LLMChain(llm=llm, prompt=prompt)
def multi_query_retrieval(question: str):
# 1. translate query
reformulated = query_gen_chain.run(question)
# parse the bullet list
queries = [q.strip("- ") for q in reformulated.split("\n") if q.strip()]
# 2. retrieve for each query
all_docs = []
for q in queries:
docs = retriever.get_relevant_documents(q)
all_docs.extend(docs)
# 3. deduplicate documents
seen = set()
unique_docs = []
for d in all_docs:
if d.page_content not in seen:
seen.add(d.page_content)
unique_docs.append(d)
return unique_docs
question = "How does rewriting queries improve RAG?"
documents = multi_query_retrieval(question)
for i, d in enumerate(documents):
print(f"Doc {i+1}: {d.page_content}")